Find information on diseases & conditions, and treatment & procedures
Cancer Therapy
Pancreatic Cancer
Overview
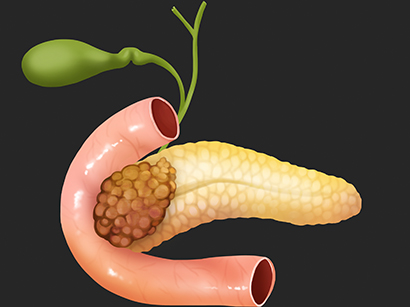
Pancreatic cancer is a mass or masses of cancerous cells formed in
pancreas, located nearby the bottom of stomach, small intestine and
gallbladder. Pancreas produces several digestive juices (enzymes)
like bile acid and hormones such as insulin that controls blood sugar.
The cancer is often spread to organs nearby it and detected in its late
stage as it does not show many symptoms at the beginning. When the
cancer is grown enough to be detected, the bowel and bile duct may
get compressed by the tumor and result in some symptoms as below.

Symptoms
- Pain in the stomach region(may radiate to the back side)
- Loss of appetite and weight
- Fatigue
- Skin turning in yellow color (jaundice)
- Sudden onset of diabetes
Treatments
1. Cancer Removal Surgery
Decision of whether to proceed the removal surgery or not is depending on
the status of cancer and its spread. The pancreas can be removed partially
or entirely. Although the entire pancreas is removed, patients are usually
able to maintain relatively normal life with help of lifelong medication therapy.
1) Process of procedure
- Patients may receive external or internal radiation therapy and chemotherapy
before the surgery.
- Begin general anesthesia (patient's breathing will depend on ventilating machine)
- Give an incision to the abdomen
- Partial or all of pancreas and normal tissue around the cancer will be removed
- Suture the incision with delicate care
2) Expected duration of hospital stay
- Generally the surgery itself takes few hours.
- Generally expected hospitalization period is 2 weeks including surgery time.
This may differ case by case.
3) Post-operative care
- The patient will be monitored thoroughly in the recovery unit to ensure that he or
she is free of complications
(bleeding, infection, excessive pain, abnormal vital signs).
- Patient may get a drain under the operated area which will stay for days.
4) Ideal outcomes
- Patient is back to normal life after six weeks
- Cancer tissues are clearly removed
- Patient's quality of life is improved
5) Risks
- Excessive bleeding, blood clots, infection, death (rare)
6) Treatment cost
Expected cost ranges from to.
2. Chemotherapy
Usually applied as a supportive treatment to surgery and radiation therapy.
Chemotherapy is delivered via pills and intravenous injection. It significantly
decreases cancer recurrence and metastasis. And it treats recurred or
metastasized cancer. F
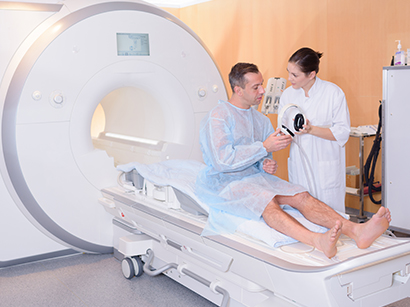
1) Process of procedure
- Chemotherapy is usually given at outpatient clinic if it is an IV injection
(more common way), or taken at home as pills
- Many patients get a vascular access device which enables safe practice of
chemotherapy in their chest.
- Fasting is required on the day of treatment
- Receive medical examination of vital signs
- Receive chemotherapy via IV
- Recheck vital signs
- Consult about side effects with doctor
- Receive prescribed medication and instructions of after chemotherapy
2) Expected duration of treatment
- Generally hospital visiting period is every once a week or once in three weeks
(depending on patient's recovery time)
- Chemotherapy is delivered through three to six months for early stage cancer,
and beyond six months for advanced cancer.
It can vary depending on patient's condition
3) Ideal outcomes
- Matastasis of cancer is prevented.
- The size of cancer mass reduces in accordance with the therapy.
4) Risks
- Nausea, fatigue, loss of hair, inhibited production of blood and blood cells from
bone marrow, decreased white blood cells, fever, infection, mouth sores and
damage in gastrointestinal tract, severe pain, and infertility
3. Radiation therapy
Ionized radiations such as X-ray, protons or others are irradiated internally and
externally to remove cancer cells. It reduces recurrence of cancer after surgery.
As it shrinks the size of cancer, is also effective in relieving symptoms.
1) Process of procedure
- Radiation can be irradiated from inside the body while patient is undergoing surgery
- Radiation can also be irradiated from inside patient's vagina using a device filled with
radioactive substance.
2) Expected duration of treatment
- Generally radiation therapy is delivered to patient five times a week for about five to six weeks
(depending on patient's condition)
3) Ideal outcomes
- Metastasis of cancer is prevented.
- The size of cancer mass reduces in accordance with the therapy.
4) Risks
- Fatigue, skin may get irritated, swelling of breast and differed skin sensation may occur.
5) Treatment cost
- Expected cost ranges from to.










 Inquiry
Inquiry Find Doctor
Find Doctor
