Find information on diseases & conditions, and treatment & procedures
Cardiology
Coronary Artery Disease (CAD)
Overview
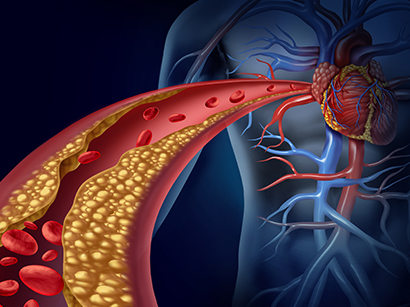
Coronary Artery Disease is a condition that makes the heart weaken or lose its function due to
a lack of oxygen supply to the heart muscle.
This is a result of narrowed coronary artery (artery around the heart muscle),
a consequence of inappropriate management of hyperlipidemia, hypertension,
diabetes, etc (genetic matter, lack of exercise, obesity, smoking, aging, and
acute continues contraction of vessels).

Symptoms
- Complaint of acute chest pain or chest pain when exercising or moving
- Squeezing pain
- Difficulty in breathing
- Radiation of pain to the left side shoulder and arm
- Feeling like heartburn
Treatments
1. Coronary Angioplasty and Stent
Minimally invasive procedure that widens narrowed or blocked coronary artery by
using catheter equipped balloon on the tip.
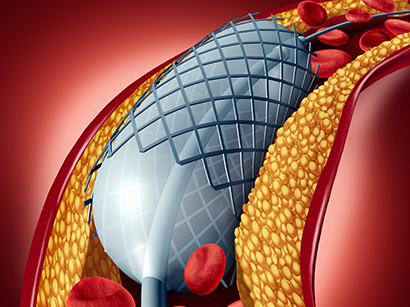
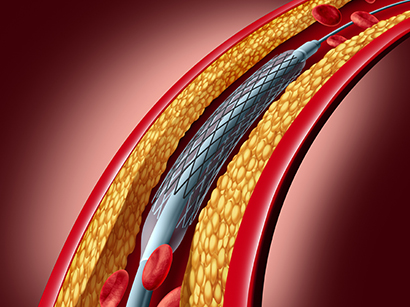
1) Process of procedure
- From the insertion of catheter, the catheter's moving path is being watched via
X-ray throughout the procedure.
- Insert a long tube catheter through an artery in the groin or wrist until it reaches
the affected area
- Inject some staining liquid via the catheter to find the exact location of blockage or
narrowed area through X-ray
- Guide the catheter to the blocked location and inflate the balloon equipped at the tip
of catheter to widen the artery and then deflate it.
- The blood flow is now enhanced.
- In many cases of angioplasty, doctors recommend to place stent (mesh tube) along
with angioplasty to prevent recurrence of blockage.
2) Expected duration of hospital stay
- Generally the procedure itself takes several hours. However, if there exist several
blockages or any complication occurs, it could take a longer time.
- If it was a scheduled procedure, and there were not a complication occurred,
the patient is expected to be hospitalized to monitor the heart for a day or two days.
- If the procedure was emergently performed due to heart attack, the duration of patient`s
hospitalization is likely to be longer.
3) Post-operative care
- The patient will be monitored thoroughly in the hospital to ensure that he or she is free
of complications (bleeding, infection, fainting, and chest pain)
- When the patient returns home, doctor will prescribe blood-thinning medications and
provide instructions for the care.
4) Ideal outcomes
- Decreased chest pain
- Enhanced blood flow to the heart
- Improved exercise capacity
5) Risks
- Recurrence of blockage or narrowing
- It is more likely happened to patients who did not place stent during angioplasty.
- Formation of blood clots in the stent
- Blood clots can block the artery and result in a heart attack. This is likely to occur
if patient stops taking prescribed blood thinners.
- Bleeding
This may occur from the area where it was catheterized.
- Heart attack, artery damage, kidney problems, stroke, abnormal heart rhythms may
occur during the procedure.
6) Treatment cost
- The cost can vary by hospitals and depending on the number of stent used.
- Expected cost ranges from to
2. Coronary Artery Bypass Graft (CABG)
An open heart surgery that replacing diseased coronary artery with healthy blood vessels
taken from patient's body to enhance the blood flow. It is usually done when CAD is too
severe or the angioplasty done previously was not successful or after a heart attack.
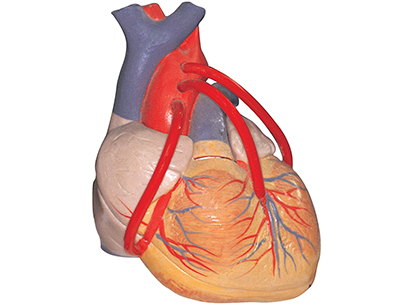
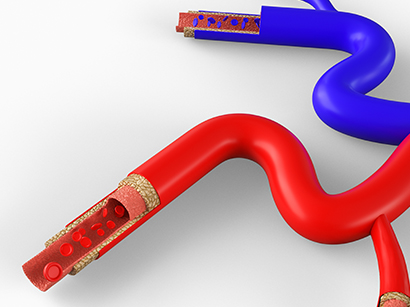
1) Process of procedure
- During the surgery, patient's heart will be either on heart-lung bypass device taking
over the role of the heart throughout the surgery or on equipment that restrains the heart
to minimize its movements during the surgery. Some hospitals perform surgery using
robotics to maintain the surgery minimally invasive.
- Begin general anesthesia (patient's breathing will depend on ventilating machine)
- Give an incision to the chest
- Take healthy artery from patients inner chest or legs or arms
- Connect the healthy artery above the diseased coronary artery so that blood flow is
bypassed and improved.
2) Expected duration of hospital stay
- A week to two weeks of hospital stay is expected in total.
- Generally the procedure itself takes up to 3 - 6 hours.
- A day or two days of Intensive care unit stay is required
3) Post-operative care
- While patient is cared in Intensive care unit, he or she will still be on ventilator until the
patient is able to breathe on their own.
- The patient will be monitored thoroughly in the hospital to ensure that he or she is free
of complications (bleeding, fever, infection, fainting, abnormal discharge from the chest and chest pain)
4) Ideal outcomes
- Patient returns to daily routine within six to 12 weeks as is general.
- Breathing is eased
- Chest pain is gone
- Exercising capacity is enhanced
5) Risks
- 2~5 % mortality
- Bleeding after surgery
- Infection that may require another surgery
- Stroke, heart failure, renal failure and pneumonia might occur after surgery
- Grafted artery may be blocked in the future
6) Treatment cost
- Expected cost ranges from to.








 Inquiry
Inquiry Find Doctor
Find Doctor
